Interview
The Israeli startup combating drug-resistant bacteria
“Some 70% of antibiotics worldwide are administered to animals, and affected pathogens may later develop antimicrobial resistance and enter the environment, affecting humans,” says David Javier Iscovich, the CEO of Mileutis, which has developed an antibiotic-alternative for dairy cows and animal health
Mileutis is choosing to approach the problem the other way around, by focusing on animal health first. “Some 70% of antimicrobials are administered to animals, and don't just affect them, but also humans and our environment. Pathogens develop AMR, and later harm us. We’re all connected. It’s a larger than life problem,” he said, drawing a parallel to the recent and distressing example of the emergence of Covid-19, which according to U.S. Congressional and WHO investigations stemmed from an outbreak that spread from bats to humans in Wuhan, China. “Similar to Covid, if we give antibiotics to animals, then those pathogens develop resistance and we can get infected too,” he said. “Today, nearly five million people have died of Covid. According to our estimates, twice that amount could die due to AMR,” he said. “So, in order to manage AMR, we first need to treat animals safely.” Mileutis’ product enhances the immune system, and is also more financially sustainable in the long term, since the company’s products are relatively cheap to develop. After treating cows, the company can then work on developing products to treat humans too.
“We can treat simple infections today with antibiotics and save lives, but they’re not going to be treatable in the future,” he said, explaining that if someone gets bitten by a tick and receives a simple over-the-counter antibiotic, in the future those may be no longer effective. Antibiotic overuse is a growing problem. “If we continue using antibiotics in such a widespread manner, the next time someone goes to hospital with a tick bite, they could die,” he said. “Antibiotics play a very important role in modern health, but we need to make sure they stay that way.” Bovine health gets a makeover And the story all starts with cows. Antibiotic resistance is a major issue in the dairy industry, since dairy cattle suffer from mastitis - a disease that leaves mammary glands inflamed - and must be treated with antibiotics. Nearly 97% of dairy cattle in industrialized farms worldwide receive antibiotics every year, particularly, at the beginning of the dry off season, 60 days before they bear calves. Farmers halt milking cows, and let them rest until they give birth. Between 30%-40% of dairy cows contract mastitis in some form, and are treated with antibiotics either once or twice, leading 7% to leave herds every year. “Milk treated with antibiotics needs to be dumped, and it’s not an economically feasible solution,” he explained. That’s where Mileutis comes in: its product is effective in stopping infections, reducing up to 90% of the antibiotics currently administered to cows. “Farmers don’t like using antibiotics either. They forget that they can’t milk the cow, and after the cow is milked - even if it’s only a few liters among tens of thousands - all that milk needs to be dumped. It’s wasteful. Sometimes, it gets into milk and could adversely affect humans.” That’s why Bovine health is getting a makeover. Mileutis helps farmers have a flourishing, more profitable dairy business; cows are treated better and yield better higher-quality milk, and consumers get a cleaner carton of milk at the store, so it’s an all-around win, he added. Imilac treats cows at the end of the lactation period before calving, while Milac will be used to treat mastitis during lactation. Mileutis’ solution is a safe product derived from proteins already present in milk and is better for bovine health and human health in the long term, Iscovich noted.
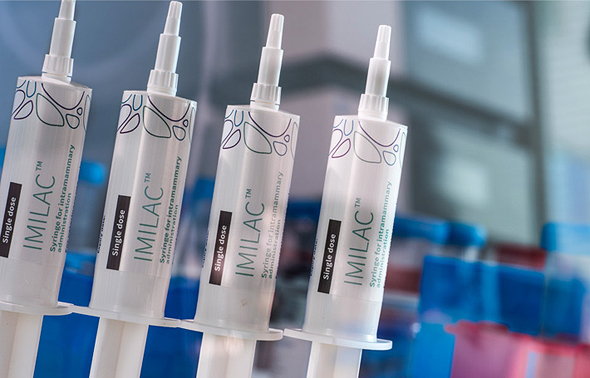 | |||
| Mileutis' Imilac can be directly administered to dairy cows and is a safe solution to treating and preventing mastitis. Photo: Eyal Toueg | צילום: אייל טואג | ||

